Understanding the ABC’s of Melanoma
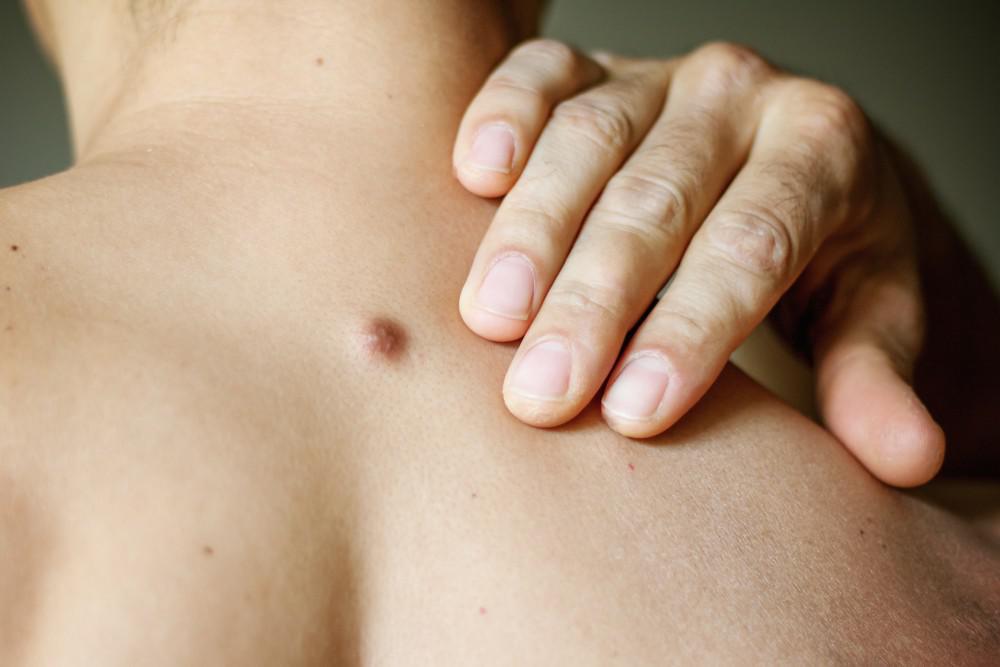
Skin cancer is something everyone should be aware of over the course of a lifetime. Melanoma is the most serious type of skin cancer, and it’s important to know what it looks like so you can seek medical care as soon as possible to prevent its spread.
Here at Hunterdon Hematology Oncology in Flemington, New Jersey, our expert oncologists explain the warning signs — commonly known as the ABCs of melanoma — and risk factors so you can get proper treatment in its early stages.
Melanoma isn’t common, but it spreads easily
You mostly hear about skin cancer in the summertime, but even in the fall and winter months, it’s just as important to protect your skin when you’re outside. Melanoma isn’t the most common type of skin cancer, but it can be the most dangerous type because of how quickly it can spread to other parts of your body if not treated soon enough.
There are several types of skin cancer that begin on the top layer, or epidermis, of your skin. These include:
- Basal cell carcinoma
- Squamous cell carcinoma
- Melanoma skin cancers
Melanoma skin cancer begins in the cells in your skin that normally make melanin — the tan color in your skin. These cells are called melanocytes. When you spend time in the sun or on a tanning bed, the ultraviolet (UV) radiation causes skin damage, which makes melanocytes produce more melanin.
If your skin absorbs too much UV radiation, or you get a bad sunburn, mutations can occur in the melanocytes that prompt these cells then grow out of control. The result is melanoma skin cancer. If not treated, melanoma may spread out of control and form a mass of cancerous cells.
Who’s at risk for melanoma?
According to the American Cancer Society, melanin helps protect the deeper layers of your skin from the harmful effects of the sun. If you’re naturally darker-skinned, you have less risk of developing melanoma, but it’s still possible. Fair-skinned people and women under age 40 are in the high-risk categories for developing melanoma.
Other risk factors include:
- Family history of melanoma
- Weak immune system
- History of sunburns
- Excessive UV radiation exposure
- Having unusual moles
People who’ve lived closer to the equator or in an area of high elevation also have a greater risk of developing melanoma.
Recognizing the signs of melanoma: Know your ABCs
Melanoma typically develops on areas of your body that have the most sun exposure, such as:
- Arms and legs
- Face and neck
- Chest and back
You can also get melanoma on the soles of your feet, palms of your hands, or even in your fingernails. When you know what to look for, you can seek treatment and decrease your risk of melanoma spreading throughout your body.
The first signs of melanoma often appear as a change to an existing mole or the development of a new, unusual-looking skin growth. The letters ABCDE can help you determine if you should seek medical care for a potential melanoma:
A is for asymmetry
Examine the moles and blemishes on your body to see what shape they are. Do you notice a mole that is asymmetrical in appearance? Melanoma could look like a mole made up of different irregular shapes.
B is for border
Do you have a mole with an irregularly shaped border? If most of the freckles and spots on your skin appear round, but you notice one that has a jagged edge, for example, that is a sign that it could be melanoma.
C is for color
A third indication of melanoma is the changing or uneven color of a mole or growth on your skin. Melanomas come in a variety of colors, including blue-black, pink, red, or brown. A melanoma may even appear white.
D is for diameter
Moles larger than a quarter-inch in diameter may be signs of melanoma. Don’t ignore the size of a mole. It’s best to get it checked out by one of our expert physicians before it continues to grow deeper into your skin.
E is for evolving
Do you notice a mole that seems to be changing over time? Changes may include color, size, and irritation, such as itching or bleeding.
Preventing melanoma and other skin cancers
While there’s no guaranteed method of completely preventing melanoma and other types of skin cancer, you can take precautions to reduce your risk. These include:
- Limiting your exposure to UV rays
- Wearing sunscreen all year long
- Staying in the shade
- Wearing a hat and sunglasses
- Avoiding tanning beds
It’s a good idea to perform self-exams regularly to note any new moles, changes to your skin, and other growths that may indicate the presence of skin cancer.
If you notice anything unusual when watching for the ABCs of melanoma, schedule an exam with the expert team at Hunterdon Hematology Oncology as soon as possible, so we can evaluate your skin, diagnose any problems, and recommend an effective treatment plan. Call our office at 908-264-1798 to book an appointment today.

